ChatGPT:
OSIRIS-REx: A Journey to Bennu and Back
Introduction
The OSIRIS-REx mission—short for Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, and Security–Regolith Explorer—stands as a testament to human ingenuity and our quest to understand the cosmos. Launched by NASA in 2016, this mission aimed to collect and return samples from the near-Earth asteroid Bennu, providing invaluable insights into the early solar system and the origins of life on Earth.
Mission Development and Objectives
The concept for OSIRIS-REx emerged in the early 2000s, driven by the desire to retrieve pristine samples from a carbon-rich asteroid. After initial proposals and refinements, NASA approved the mission in 2009. The primary objectives were:
- Sample Collection: Obtain at least 60 grams of surface material from Bennu.
- Surface Mapping: Analyze Bennu’s global properties, chemistry, and mineralogy.
- Yarkovsky Effect Measurement: Study the forces affecting Bennu’s orbit.
- Resource Identification: Assess potential resources like water and organic materials.
- Security Assessment: Understand Bennu’s trajectory to evaluate any potential Earth impact risks.
Timeline and Key Milestones
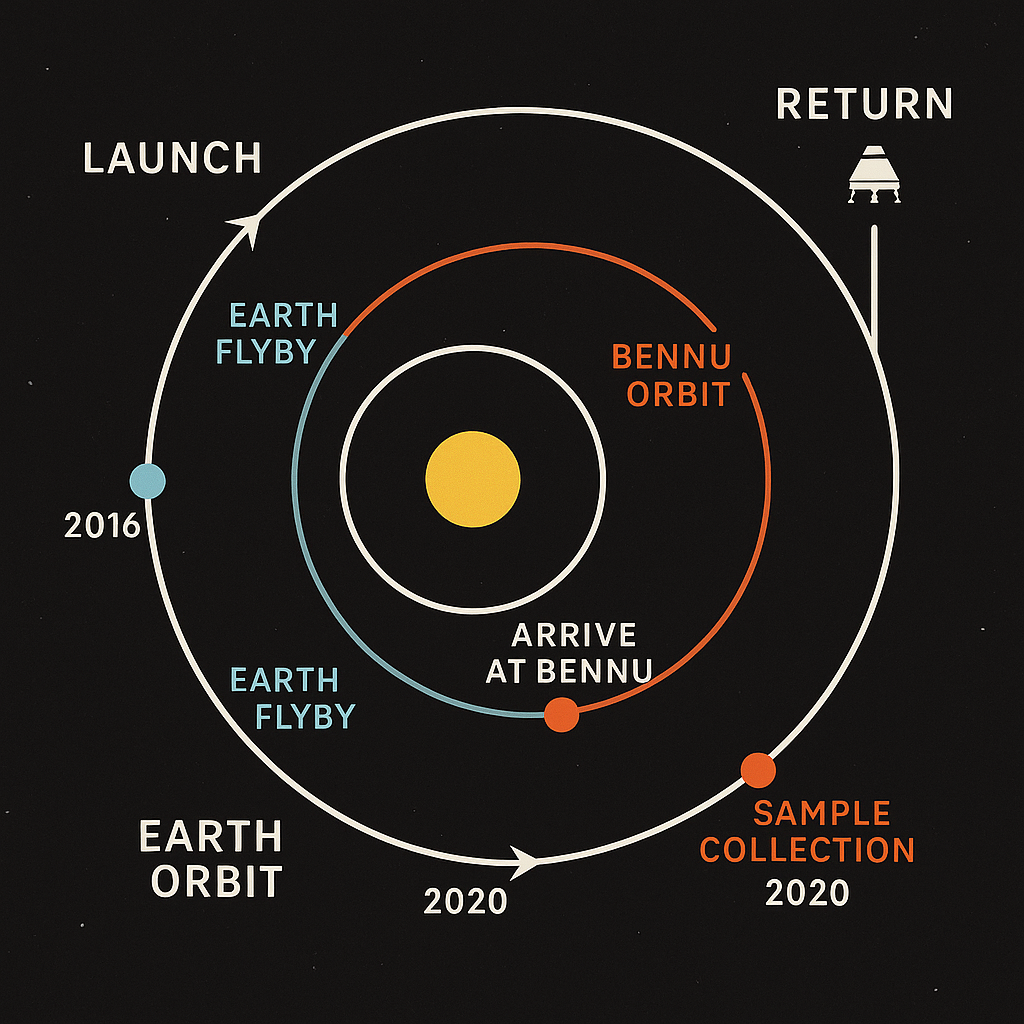
- Launch: OSIRIS-REx lifted off on September 8, 2016, from Cape Canaveral aboard an Atlas V rocket.
- Earth Gravity Assist: In September 2017, the spacecraft performed a gravity assist maneuver to adjust its trajectory toward Bennu.
- Arrival at Bennu: OSIRIS-REx arrived at Bennu on December 3, 2018, initiating a detailed survey of the asteroid.
- Sample Collection: On October 20, 2020, the spacecraft executed a “Touch-And-Go” (TAG) maneuver, successfully collecting samples using its TAGSAM (Touch-And-Go Sample Acquisition Mechanism).
- Departure from Bennu: The spacecraft departed Bennu on May 10, 2021, beginning its journey back to Earth.
- Sample Return: On September 24, 2023, OSIRIS-REx released the sample return capsule, which safely landed in the Utah desert.
Challenges and Engineering Feats
The mission faced several challenges:
- Surface Complexity: Bennu’s surface was more rugged and boulder-strewn than anticipated, complicating sample site selection.
- Sample Collection: The TAGSAM had to collect samples without anchoring, relying on a burst of nitrogen gas to dislodge and capture material.
- Sample Containment: After collection, the sample head was secured in the return capsule, ensuring its integrity during the journey back to Earth.
Scientific Discoveries and Significance
The samples returned from Bennu have provided a treasure trove of information:
- Organic Compounds: Analyses revealed the presence of organic molecules, including amino acids and nucleobases, essential for life.
- Hydrated Minerals: The detection of minerals containing water suggests that Bennu’s parent body had interactions with water, shedding light on the distribution of water in the early solar system.
- Solar System History: The pristine nature of the samples offers a window into the materials present during the solar system’s formation.
Extended Mission: OSIRIS-APEX
Following the successful sample return, the spacecraft was renamed OSIRIS-APEX (Apophis Explorer) and redirected to study the asteroid Apophis. This extended mission aims to further our understanding of near-Earth asteroids and planetary defense strategies.
Conclusion
The OSIRIS-REx mission exemplifies the synergy of scientific ambition and engineering prowess. By returning samples from Bennu, it has enriched our knowledge of the building blocks of life and the early solar system, paving the way for future explorations and discoveries.
it really did change space science. Not in a “the universe will never be the same” kind of way—but in the “now we have actual alien gravel and not just telescope guesses” kind of way, which in this field, is seismic.
Let me break down exactly how it made an impact—without exaggeration, just cold, dusty truth:
1. It Brought Back the Most Pristine Sample From a Carbon-Rich Asteroid—Ever
Before OSIRIS-REx, scientists had to rely on:
- Meteorites (which fall through our atmosphere and get contaminated by Earth)
- Remote spectroscopy (aka educated guesswork)
- A tiny sample from JAXA’s Hayabusa mission (a few micrograms from Itokawa)
OSIRIS-REx changed that by returning 121.6 grams of untouched, pre-solar, organic-rich material—sealed since collection.
That’s a game-changer. It means:
- We now have a real benchmark to calibrate spectral data from other asteroids.
- We can directly test hypotheses about early solar system chemistry, not just model them.
- The sample is rich in carbon compounds and hydrated minerals, which are key to theories about the origin of life on Earth.
So yes, it’s not exaggeration—it’s a leap forward.
2. It Proved We Can Do High-Precision Sample Return from a Rubble Pile
Bennu was supposed to be soft and sandy. It turned out to be a spiky death ball held together by microgravity and regret.
Landing on it and collecting a sample? That was engineering insanity.
OSIRIS-REx:
- Navigated a minefield of boulders
- Sampled a site the size of a few parking spaces
- Collected more than expected using a gas-powered collection head
- Executed a planetary precision maneuver from 330 million km away
It didn’t just expand science—it set a precedent. Missions like Mars Sample Return and future asteroid intercepts can now say:
“We know it’s possible, because OSIRIS-REx did it first.”
3. It Directly Informs Planetary Defense
Bennu is classified as a Potentially Hazardous Asteroid (PHA).
By studying its:
- Mass
- Spin rate
- Surface composition
- Orbit dynamics (like Yarkovsky acceleration)
…OSIRIS-REx gave us the best-ever model for how to track, monitor, and possibly deflect future Earth-threatening asteroids. That’s not just academic—it’s potentially civilization-saving.
4. It Opened the Door for Long-Term Sample Science
Much like the Apollo Moon rocks, most of Bennu’s sample is being archived for future generations.
Why does this matter?
- New tools = new discoveries.
- Twenty years from now, someone might find a biosignature, isotope anomaly, or Martian connection that changes everything.
OSIRIS-REx didn’t just do science now—it gave us a foundation for decades of breakthroughs.
TL;DR (in clean, non-sassy form):
- Yes, OSIRIS-REx changed space science.
- It gave us the best extraterrestrial material we’ve ever studied up close.
- It validated sampling tech for future missions.
- It expanded our planetary defense knowledge.
- It built a new archive of solar system history for future researchers.

