ChatGPT:Fighting Age-Related Voice Changes: Comprehensive Guide
As we age, our bodies undergo numerous changes, and the voice is no exception. The voice, a key aspect of communication and expression, can lose its strength and clarity over time. This guide explores the reasons behind these changes, the symptoms one might experience, and practical steps to maintain a healthy voice into older age.
🌟 Understanding Voice Changes with Age
🔄 The Mechanism of Voice Changes
The voice is produced by the vibration of the vocal cords, which are located in the larynx (voice box). As we age, several physiological changes can affect these cords:
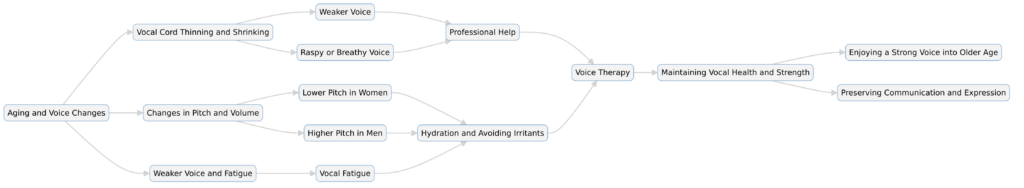
- Thinning of Vocal Cords: The vocal cords, which are essentially twin bands of muscle, may become thinner with age. This can lead to a less robust closure during speech, resulting in a weaker, less vibrant voice.
- Frequency Changes: There can be shifts in the pitch of the voice. Women might notice a lowering of their pitch, while men may experience a higher pitch. This is attributed to changes in the tension and elasticity of the vocal cords.
- Decreased Lung Capacity: The lungs play a critical role in voice production by providing the air needed to vibrate the vocal cords. With age, lung capacity can diminish, reducing the ability to project the voice.
🧬 Symptoms of an Aging Voice
Beyond just changes in pitch and volume, an aging voice might exhibit several other symptoms:
- Breathiness: A breathy quality in the voice can arise from incomplete closure of the vocal cords, allowing excess air to escape during speech.
- Extra Mucus: Incomplete closure can also make it difficult to expel mucus from the throat, leading to frequent throat clearing.
- Vocal Fatigue: The vocal cords, like other muscles, can become fatigued with overuse. This can be exacerbated by prolonged speaking, especially in noisy environments.
- Raspy or Hoarse Voice: The voice may sound raspy or hoarse due to changes in the vocal cords or the presence of mucus.
🛡️ Strategies for Maintaining Vocal Health
💧 Hydration and Environment
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is crucial for maintaining the lubrication of the vocal cords. It’s recommended that women consume about 11 cups (88 ounces) and men about 15 cups (120 ounces) of fluids per day. This can include water and other beverages, as well as moisture-rich foods.
- Humidify Your Environment: Dry air can irritate the vocal cords. Using a humidifier, especially in dry climates, can help maintain a moist environment conducive to vocal health.
- Avoid Irritants: Smoke, chemical fumes, and strong perfumes can inflame the vocal cords. Reducing exposure to these irritants is beneficial.
🚫 Avoid Overuse and Harmful Habits
- Limit Voice Strain: Repeatedly raising your voice or yelling can strain the vocal cords, potentially leading to inflammation and even lesions. This is common among professionals who use their voices intensively, such as teachers.
- Avoid Spicy Foods: Foods that cause acid reflux or irritation can also affect the vocal cords. Managing diet to avoid these triggers is recommended.
- Minimize Throat Clearing: Habitual throat clearing can be harsh on the vocal cords. It’s better to sip water or use a lozenge to clear the throat gently.
🔬 When to Seek Professional Help
If changes in your voice persist for more than four weeks, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. Persistent hoarseness or voice loss can indicate more serious underlying conditions, such as vocal cord paralysis, polyps, or even cancer.
- Medical Interventions: Conditions like acid reflux can inflame the vocal cords. Treatment might include medications or, in more severe cases, surgical interventions.
- Voice Therapy: A speech pathologist can provide valuable guidance on voice exercises and techniques to strengthen the vocal cords and improve vocal control. Techniques might include breathing exercises and practices to improve airflow and vocal efficiency.
🎤 Voice Therapy and Exercises
Voice therapy involves specific exercises designed to enhance the strength and flexibility of the vocal cords. Here are some techniques used:
- Pitch Glides: Smoothly transitioning from low to high notes helps improve control over pitch and vocal range.
- Breath Control Exercises: Learning to manage breath effectively can support better voice projection and endurance.
- Vocal Warm-Ups: Like any other muscle group, the vocal cords benefit from warm-up exercises, especially before extensive use.
🎶 Conclusion: Embracing the Changes
While aging can bring changes to the voice, understanding these changes and taking proactive steps can help maintain vocal health and strength. Regular hydration, avoiding irritants, and seeking professional help when needed are key strategies. Voice therapy offers a practical solution to strengthen and refine the voice, ensuring it remains a powerful tool for communication and expression throughout life.
Maintaining vocal health is a lifelong journey, and with the right care, it’s possible to enjoy a strong and clear voice well into older age. Whether you’re a professional speaker, singer, or simply someone who values their voice, these strategies can help preserve this vital aspect of your identity and communication.
By following these guidelines and seeking appropriate care, you can navigate the changes that come with aging and continue to use your voice effectively and joyfully.
Q&A
Q: What are common changes in the voice as one ages?
A: As people age, the vocal cords may thin and shrink, leading to a weaker, raspy, or breathy voice. Women might experience a lowering of pitch, while men may notice a higher pitch. Additionally, decreased lung capacity can reduce the volume and projection of the voice.
Q: How does aging affect the vocal cords and voice pitch?
A: Aging can cause the vocal cords to become thinner and less elastic, which can result in a less robust closure and vibration during speech. This can make the voice sound weaker or breathy. The frequency of vocal cord vibrations may also change, typically causing a lower pitch in women and a higher pitch in men.
Q: What symptoms indicate age-related changes in the voice?
A: Symptoms include breathiness, vocal fatigue, extra mucus in the throat, and a raspy or hoarse voice. These symptoms can arise from weakened vocal cords, reduced lung capacity, and incomplete closure of the vocal cords during speech.
Q: What are some strategies to maintain vocal health?
A: Strategies include staying hydrated, avoiding irritants like smoke and chemicals, limiting spicy foods, and avoiding habitual throat clearing. It’s also important to avoid overusing the voice, particularly in loud environments.
Q: Why is hydration important for vocal health?
A: Hydration helps keep the vocal cords lubricated, which is essential for their proper function. Dry vocal cords are more prone to irritation and strain, which can lead to voice problems.
Q: What role does a humidifier play in vocal health?
A: A humidifier adds moisture to the air, which can help prevent the vocal cords from drying out, especially in dry climates or environments with artificial heating or air conditioning.
Q: When should someone seek medical help for voice changes?
A: If voice changes persist for more than four weeks, or if there’s a persistent hoarseness or change in voice quality, it’s important to consult a doctor. These symptoms could indicate underlying conditions that require medical attention.
Q: What are some medical treatments for severe voice changes?
A: Treatments may include medications for conditions like acid reflux, surgical interventions, or injections of fillers to improve vocal cord closure. In some cases, voice therapy with a speech pathologist may be recommended.
Q: How can voice therapy help with age-related voice changes?
A: Voice therapy can help strengthen the vocal cords and improve breath control, allowing for better voice projection and endurance. Techniques may include breathing exercises, pitch glides, and other specific exercises to enhance vocal quality.
Q: What exercises can help maintain a strong voice?
A: Exercises like pitch glides (smooth transitions from low to high notes), breath control exercises, and vocal warm-ups can help maintain vocal strength and flexibility. These exercises are particularly beneficial for those who use their voice extensively.
Gemini: Aging affects the vocal system in several ways, leading to changes in voice quality and function:
Vocal Cords (also known as vocal folds):
- Thinning and atrophy: The vocal folds can become thinner and less pliable with age. This can reduce their ability to close completely, leading to a breathy or weak voice.
- Reduced vibration: The muscles within the vocal folds may weaken, resulting in less efficient vibration. This can affect pitch control and cause the voice to sound shaky or unsteady.
- Increased stiffness: The tissues of the vocal folds may stiffen due to changes in collagen and elastin fibers. This can make it harder for the vocal folds to vibrate quickly, impacting the higher frequencies of the voice.
Lungs:
- Reduced capacity: The lungs’ ability to take in and expel air diminishes with age. This can lead to decreased breath support for speech, causing shorter phrases, reduced volume, and difficulty projecting the voice.
- Weaker respiratory muscles: The muscles involved in breathing, such as the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, may weaken. This can further compromise breath support and control.
Other parts of the vocal system:
- Larynx (voice box): The cartilages of the larynx can calcify and become less flexible. This can affect the movement of the vocal folds and contribute to voice changes.
- Resonating cavities: The size and shape of the resonating cavities (throat, mouth, and nasal passages) can change due to loss of muscle tone and tissue elasticity. This can alter the resonance of the voice, affecting its timbre and quality.
- Mucus production: The glands in the vocal tract may produce less mucus, leading to dryness and irritation. This can make it difficult to speak comfortably and maintain vocal health.
- Neurological changes: The nerves that control the muscles of the vocal system may experience some decline in function. This can affect coordination and control of the voice.
These changes are often gradual and may vary from person to person. However, they can significantly impact voice quality and communication abilities.
The article discusses age-related voice changes, which can include changes in pitch, power, and the development of breathiness or vocal fatigue. This is due to changes in the vocal cords, lungs, and other parts of the vocal system.
To protect your voice, the article recommends:
- Avoiding overuse and irritants: Yelling, aggressive speaking, smoke, chemicals, and spicy foods can all damage your vocal cords.
- Staying hydrated: Dry vocal cords don’t function well, so make sure to drink plenty of fluids.
- Avoiding frequent throat clearing: This can irritate your vocal cords over time.
If you are experiencing voice changes related to aging, it’s important to consult with a doctor or speech-language pathologist to determine the cause and explore appropriate treatment options. Voice therapy, vocal hygiene practices, and lifestyle modifications can often help manage and improve age-related voice changes.

